数据结构即数据元素相互之间存在的一种和多种特定的关系集合。
# What are data structures?
数据结构是什么?
数据结构是一种用于组织、处理、检索和存储数据的专用格式。
A data structure is a specialized format for organizing, processing, retrieving and storing data.
数据结构用来干什么?
数据结构是应用程序的构建块。通过将数据元素组合成一个 逻辑单元 来表示某一抽象数据类型。
Data structures are the building blocks for more sophisticated applications. They are designed by composing data elements into a logical unit representing an abstract data type that has relevance to the algorithm or application.
例如“客户名称”就是一种抽象数据类型。它由“名字”、“中间名”和“姓氏”的字符串组成。
An example of an abstract data type is a "customer name" that is composed of the character strings for "first name," "middle name" and "last name."
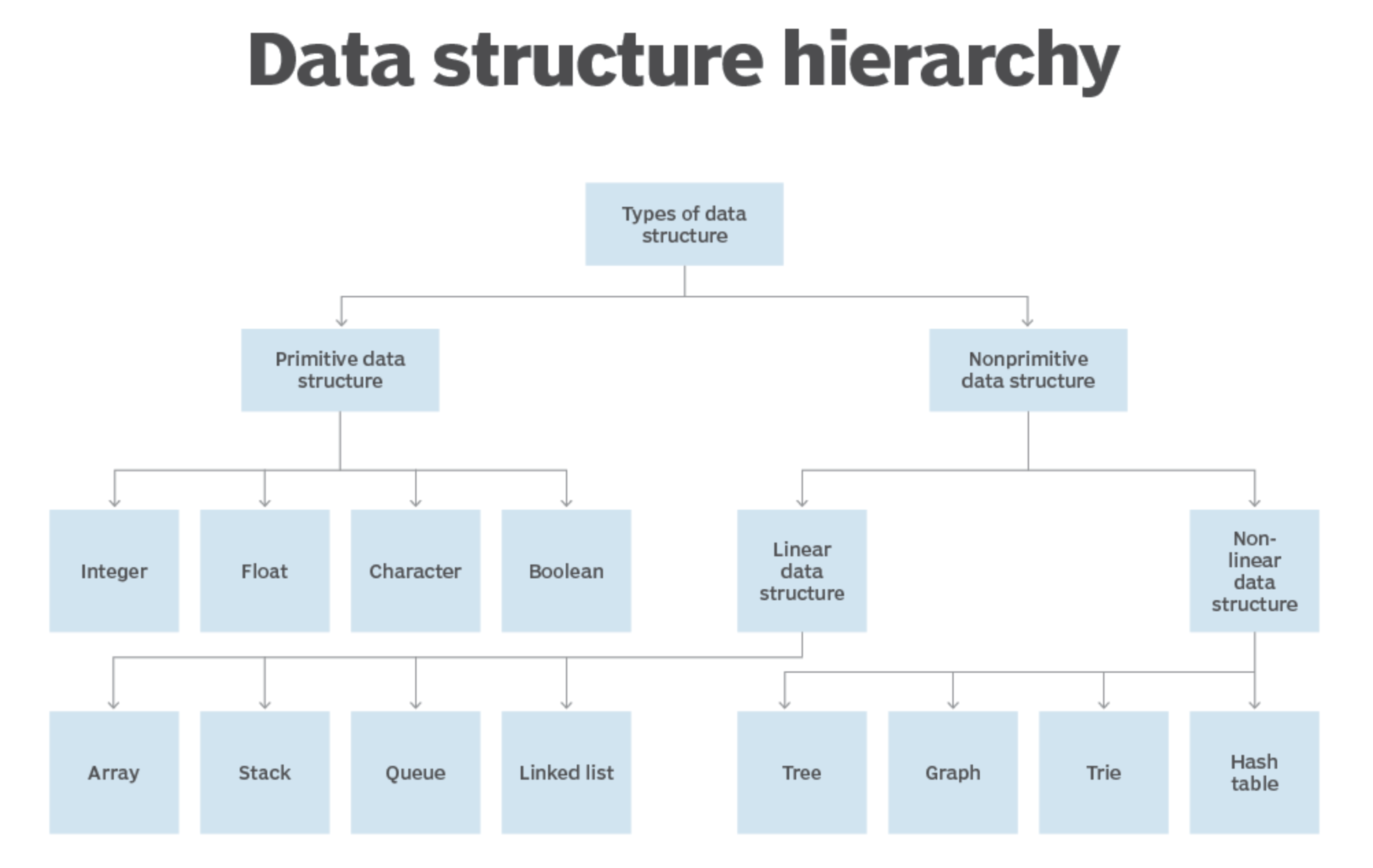
# Types of data structures
数据元素之间的逻辑结构(关系)大概可分成两种:线性结构、非线性结构。
线性结构:是一个有序数据元素的集合。 其中数据元素之间的关系是一对一的关系,即除了第一个和最后一个数据元素之外,其它数据元素都是首尾相接的。常用的线性结构有: 栈,队列,链表,线性表。
非线性结构:各个数据元素不再保持在一个线性序列中,每个数据元素可能与零个或者多个其他数据元素发生联系。常见的非线性结构有:二维数组、树、图、堆、字典树、哈希表。
# Binary Tree
二叉树是一种典型的树树状结构。
Why Trees?
1. One reason to use trees might be because you want to store information that naturally forms a hierarchy. For example, the file system on a computer:
file system
-----------
/ <-- root
/ \
... home
/ \
ugrad course
/ / | \
... cs101 cs112 cs113
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2. Trees (with some ordering e.g., BST) provide moderate access/search (quicker than Linked List and slower than arrays).
3. Trees provide moderate insertion/deletion (quicker than Arrays and slower than Unordered Linked Lists).
4. Like Linked Lists and unlike Arrays, Trees don’t have an upper limit on number of nodes as nodes are linked using pointers.
# 二叉树遍历
# 中序遍历
给定一个二叉树,返回它的 中序 遍历。
输入: [1,null,2,3]
1
\
2
/
3
输出: [1,3,2]
2
3
4
5
6
7
递归实现
var inorderTraversal = function (root, array = []) {
if (root) {
inorderTraversal(root.left, array);
array.push(root.val);
inorderTraversal(root.right, array);
}
return array;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
非递归实现
取跟节点为目标节点,开始遍历
- 左孩子入栈 -> 直至左孩子为空的节点
- 节点出栈 -> 访问该节点
- 以右孩子为目标节点,再依次执行1、2、3
var inorderTraversal = function (root) {
const result = [];
const stack = [];
let current = root;
while (current || stack.length > 0) {
while (current) {
stack.push(current);
current = current.left;
}
current = stack.pop();
result.push(current.val);
current = current.right;
}
return result;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# 前序遍历
示例:
输入: [1,null,2,3]
1
\
2
/
3
输出: [1,2,3]
2
3
4
5
6
7
递归实现
var preorderTraversal = function (root, array = []) {
if (root) {
array.push(root.val);
preorderTraversal(root.left, array);
preorderTraversal(root.right, array);
}
return array;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
非递归实现
取跟节点为目标节点,开始遍历
- 访问目标节点
- 左孩子入栈 -> 直至左孩子为空的节点
- 节点出栈,以右孩子为目标节点,再依次执行1、2、3
var preorderTraversal = function (root) {
const result = [];
const stack = [];
let current = root;
while (current || stack.length > 0) {
while (current) {
result.push(current.val);
stack.push(current);
current = current.left;
}
current = stack.pop();
current = current.right;
}
return result;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# 后序遍历
示例:
输入: [1,null,2,3]
1
\
2
/
3
输出: [3,2,1]
2
3
4
5
6
7
递归实现
var postorderTraversal = function (root, array = []) {
if (root) {
postorderTraversal(root.left, array);
postorderTraversal(root.right, array);
array.push(root.val);
}
return array;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
非递归实现
取跟节点为目标节点,开始遍历
左孩子入栈 -> 直至左孩子为空的节点
栈顶节点的右节点为空或右节点被访问过 -> 节点出栈并访问他,将节点标记为已访问
栈顶节点的右节点不为空且未被访问,以右孩子为目标节点,再依次执行1、2、3
var postorderTraversal = function (root) {
const result = [];
const stack = [];
let last = null; // 标记上一个访问的节点
let current = root;
while (current || stack.length > 0) {
while (current) {
stack.push(current);
current = current.left;
}
current = stack[stack.length - 1];
if (!current.right || current.right == last) {
current = stack.pop();
result.push(current.val);
last = current;
current = null; // 继续弹栈
} else {
current = current.right;
}
}
return result;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
# 二叉树深度
# 二叉树最大深度
给定一个二叉树,找出其最大深度。
二叉树的深度为根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
输入:[3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
输出:3
2
3
4
5
6
7
实现
- 深度优先遍历 + 分治
- 一棵二叉树的最大深度等于左子树深度和右子树最大深度的最大值 + 1
function TreeDepth(pRoot) {
return !pRoot ? 0 : Math.max(TreeDepth(pRoot.left), TreeDepth(pRoot.right)) + 1
}
2
3
# 二叉树最小深度
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。
输入:[3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
输出:2
2
3
4
5
6
7
实现:深度优先 + 分治
var minDepth = function (root) {
if (!root) {
return 0;
}
if (!root.left) {
return 1 + minDepth(root.right);
}
if (!root.right) {
return 1 + minDepth(root.left);
}
return Math.min(minDepth(root.left), minDepth(root.right)) + 1
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
# Application: Binary Search Tree
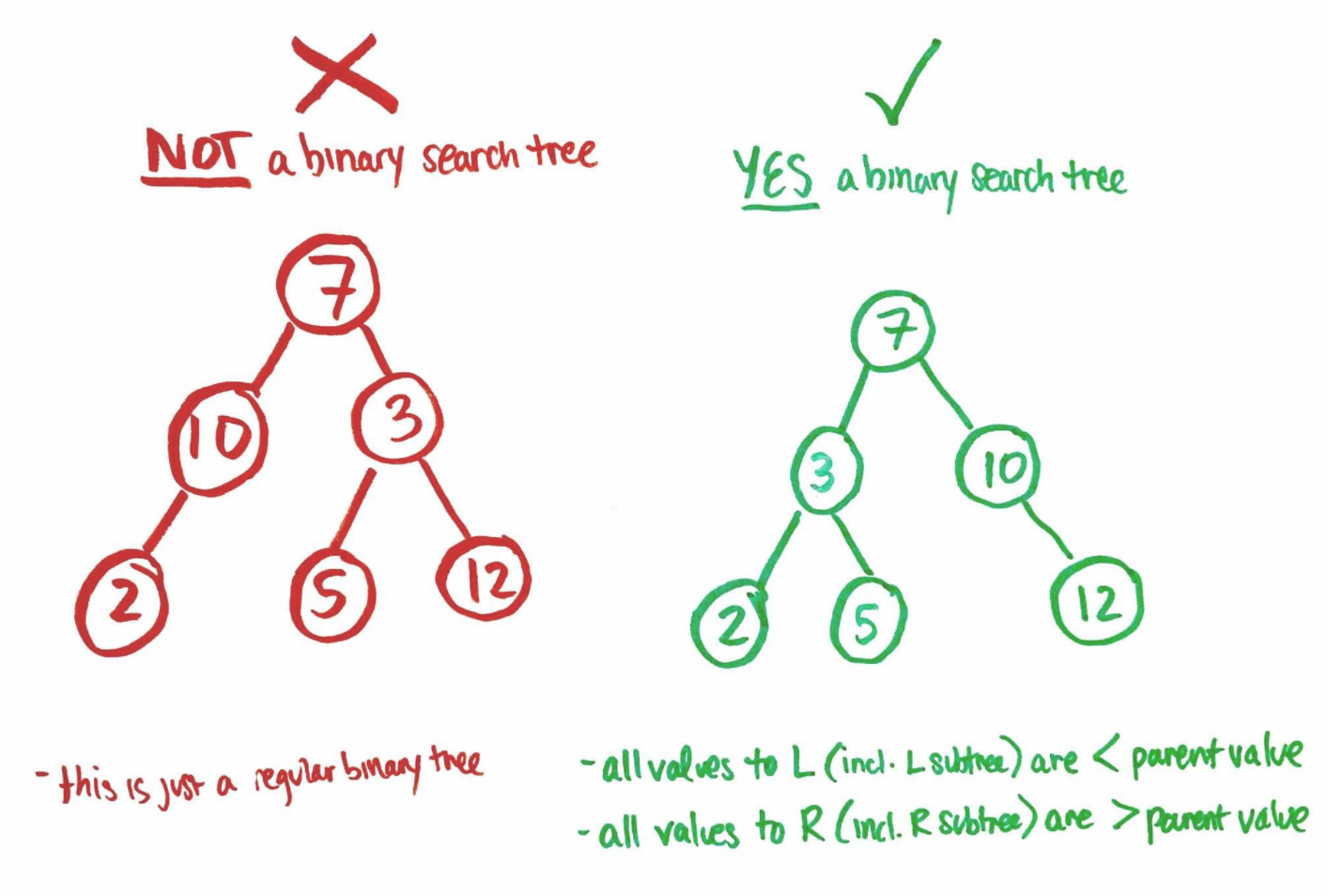
二叉查找树:任意节点的左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的值;任意节点的右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于它的根结点的值。
二叉查找树相比于其他数据结构的优势在于查找、插入的时间复杂度较低,为O(log n)。
getNode: function (data, node) {
if (node) {
if (data === node.data) {
return node;
} else if (data < node.data) {
return this.getNode(data,node.left);
} else {
return this.getNode(data,node.right);
}
} else {
return null;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
