找到程序里的所有失败是一个不可判定的问题。
# Concepts
# Fault, Error & Failure
看一段用于计算一个数组平均值的代码:
public static void CSta (int [ ] numbers)
{
int length = numbers.length;
double mean, sum;
sum = 0.0;
for (int i = 1; i < length; i++) // i=0
{
sum += numbers [ i ];
}
mean = sum / (double) length;
System.out.println ("mean: " + mean);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
Fault
软件故障:A static defect in the software. 此处,整个静态的部分都为Fault(Bug)。
Error
软件错误:An incorrect internal state that is the manifestation of some fault. 当我们进行输入时,内部值 sum 从第二项开始累加,此处为Error。
Test Input: [3,4,5]
Sum = 3+4+5
Sum = 4+5 // error
2
3
Failure
软件失败:External, incorrect behavior with respect to the requirement or other description of the expected behavior. 当我们进行测试时,返回了不正确的输出值。此处为Failure(Bug)。
Test Input: [3,4,5]
mean=4
mean=3 // Failure
2
3
Bug
informal term for fault/failure.
# PIE Model
为了揭示失败(Failure),测试用例必须满足PIE模型。即到达程序中包含故障的位置(可达性),被执行后造成不正确的程序状态(影响),被影响的部分传播到其他部分,进而导致不正确的输出或者是错误的程序最终状态(传播)。
Execution/Reachability: The location or locations in the program that contain the fault must be reached.
Infection: The state of the program must be incorrect.
Propagation: The infected state must propagate to cause some output of the program to be incorrect.
当程序员忘记写部分代码(也称代码缺失故障)时,PIE模型依然适用:当测试执行到代码缺失的地方时,程序计数器——作为程序状态的一部分,必定会包含错误的数值。
# Test Oracle
Test oracle (or just oracle) is a mechanism for determining whether a test has passed or failed.
Hardest problem in auto-testing: test oracle generation.
A test oracle might specify correct output for all possible input or only for specific input. It might not specify actual output values but only constraints on them.
The oracle might be:
- a program (separate from the system under test) which takes the same input and produces the same output
- documentation that gives specific correct outputs for specific given inputs
- a documented algorithm that a human could use to calculate correct outputs for given inputs
- a human domain expert who can somehow look at the output and tell whether it is correct
- or any other way of telling that output is correct.
# Test Fixture
A fixed state of the software under test used as a baseline for running tests; also known as the test context, e.g.
Loading a database with a specific, known set of data.
Preparation of input data and set-up/creation of fake or mock objects.
# Testing vs. Debugging
Testing(测试) is to reveal a bug by executing test and observing failure.
Debugging(调试) is to fix a bugby locating, understanding and correcting fault.
# Verification vs. Validation
Validation
The assurance that a product, service, or system meets the needs of the customer and other identified stakeholders. It often involves acceptance and suitability with external customers.”
“ Are we building the right product?”
Verification
“The evaluation of whether or not a product, service, or system complies with a regulation, requirement, specification, or imposed condition. It is often an internal process.”
“Are we building the product right?”
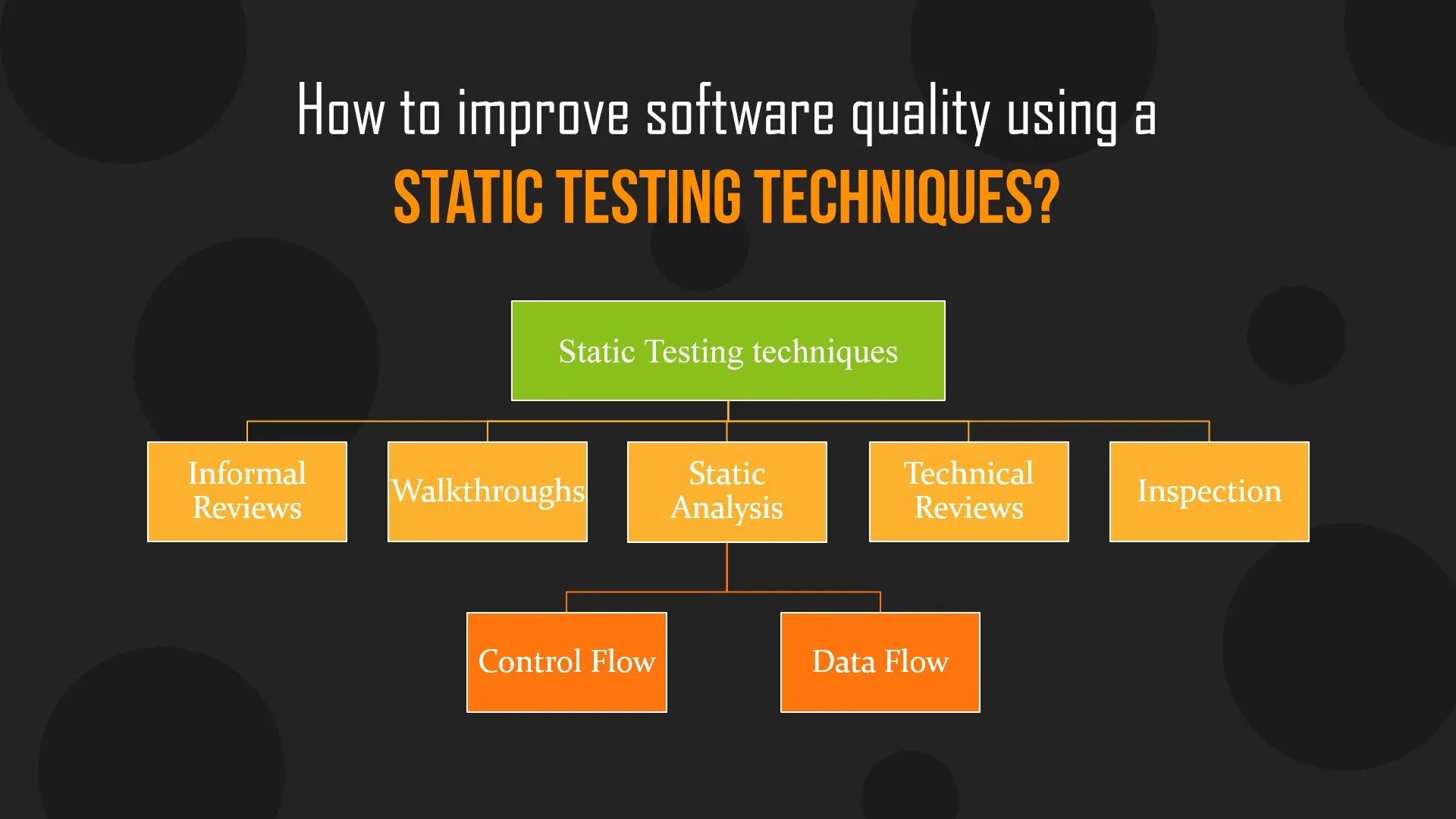
# Static Testing vs. Dynamic Testing
Static testing
Static testing is about the prevention of defects.
Static testing does the verification process.
Static testing is performed before compilation.
Dynamic testing
Dynamic testing is about finding and fixing the defects.
Dynamic testing does the validation process.
Dynamic testing is performed after compilation.
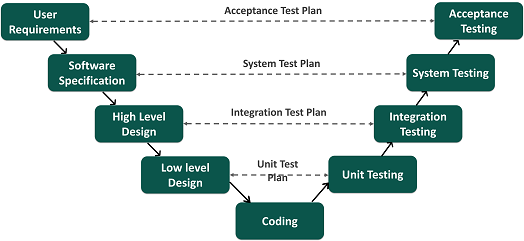
# V-Model
# Unit Testing
Unit testing is testing of an basic module of the software. Such as a function, a class, a component.
Typical problems revealed: Local data structures, Algorithms, Boundary conditions, Error handling.
# How to Do Unit Testing
Build systems in layers. Start with classes that don’t depend on others. Continue testing building on already tested classes.
